Understanding the Protein Absorption Limit: How Much is Too Much?
Protein is an essential nutrient that supports the body by building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and maintaining immune...
.png?width=70&height=70&name=Stark_LogoMark%20(1).png)

In the dynamic world of nutrition, there is one term that nearly everyone has heard of, whether they buy into it or not – ketosis. As you may have guessed, this is precisely where the keto diet gets its' name, but what exactly is ketosis, and why has it become a cornerstone in the realm of fad diets? Ketosis is a metabolic state where the body shifts from relying on carbohydrates for energy to using ketones, molecules produced from the breakdown of fats. This low-carb lifestyle has garnered immense popularity, with enthusiasts touting its benefits for weight loss and overall well-being. In this article, we will embark on a journey through the intricacies of ketosis, exploring how to enter this state, the significance of elevated ketones, the effects on the body, and why burning more dietary fat doesn't equate to burning more body fat.
Embarking on the ketosis adventure involves a strategic alteration of dietary habits. The key is to significantly reduce carbohydrate intake to 20-50g per day while simultaneously increasing the consumption of healthy fats and maintaining a moderate protein intake. This reduction in carbs prompts the body to deplete its glycogen stores, and as a result, the liver begins producing ketones. Elevated ketone levels indicate that the body is in a state of ketosis, where it utilizes these molecules as an alternative energy source. Monitoring ketone levels can be done through various methods, such as urine strips, blood testing, or breath analyzers. When looking into the intricacies of ketosis, understanding the correlation between dietary choices and elevated ketone levels becomes crucial for success in this low-carb lifestyle.
The effects of ketosis extend far beyond its role in body composition. Many individuals report heightened mental clarity and focus when in a state of ketosis, which can be attributed to the brain's efficient utilization of fats as a fuel source, providing a stable and sustained energy supply. What is interesting is that while being in ketosis, some people experience increased energy levels and reduced inflammation, while others experience side effects like fatigue, nausea, and headaches, which have been dubbed the "keto flu".
For those grappling with metabolic issues such as insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes, ketosis can offer a reprieve by improving insulin sensitivity and aiding in better blood sugar control. The quick impact on mental and physical well-being makes ketosis a compelling choice for those seeking to re-evaluate their eating habits.
While it's commonly assumed that burning more dietary fat equates to burning more body fat, the mechanisms in ketosis present a nuanced perspective. In a standard diet, the body utilizes dietary fats for energy, leaving stored body fat untouched. However, ketosis flips the script. By restricting carbohydrate intake, the body's primary energy source shifts to stored fats, triggering the production of ketones. This strategic shift prioritizes the breakdown of stored body fat for energy rather than relying solely on dietary fat. Therefore, the ketogenic diet's emphasis on dietary fat intake is not about burning that fat directly but about facilitating the metabolic switch that enables the body to tap into its own fat stores more efficiently. However, even while in ketosis, a caloric surplus (or eating more calories than you expend) will result in gaining body fat, and a caloric deficit (or eating fewer calories than you expend) will result in losing body fat. Understanding this distinction is crucial for those navigating the intricacies of ketosis and its impact on body composition.
Ketosis can be achieved by reducing carbohydrate intake significantly, leading to elevated ketone levels that signify the body's reliance on fats for fuel. It's essential to recognize that the emphasis on burning dietary fats as fuel in ketosis isn't a direct correlation to burning body fat.
While some people may feel better energized from a high distribution of dietary fats over carbohydrates, others may feel sluggish or dizzy. Navigating the path to ketosis involves a conscious shift in dietary choices, and some people may use keto as their motivation to remove ultra-processed break products or rely less on fast food due to a lack of keto options, while others may suffer serious nutrient deficiencies from a lack of food diversity. Be sure to consult your doctor or nutritionist before making any drastic changes to your diet, and remember to listen to your body - what works for one may not work for all.

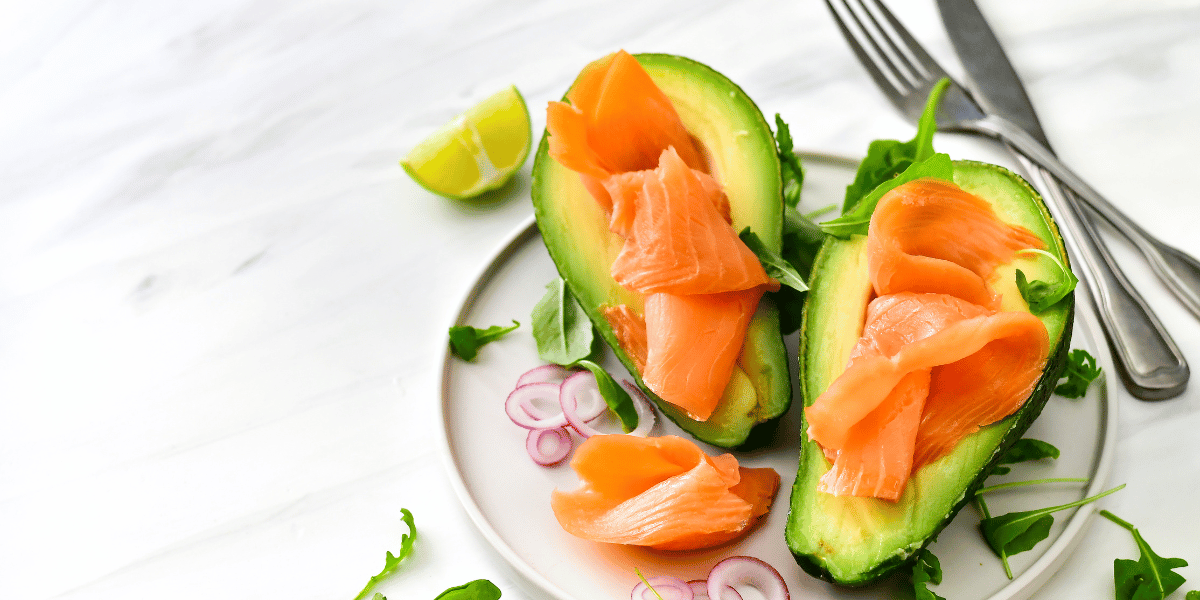
Protein is an essential nutrient that supports the body by building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and maintaining immune...
Are you looking to take control of your body and shape it into the dream physique you have always wanted? If so, strength training should be a top...

Any goal you set should be accompanied by a detailed plan on how to accomplish it. However, in order to create a plan, you have to know your...